[ad_1]
Wires have so much going for them in terms of shifting electrical energy round, however they’ve their drawbacks too. Who, in any case, hasn’t uninterested in having to plug in and unplug their cellphone and different rechargeable gizmos? It’s a nuisance.
Wires additionally problem electrical utilities: These firms should take pains to spice up the voltage they apply to their transmission cables to very excessive values to keep away from dissipating many of the energy alongside the way in which. And in terms of powering public transportation, together with electrical trains and trams, wires should be utilized in tandem with rolling or
sliding contacts, that are troublesome to take care of, can spark, and in some settings will generate problematic contaminants.
Many individuals are hungry for options to those points—witness the widespread adoption over the previous decade of wi-fi charging, principally for moveable client electronics however
also for vehicles. Whereas a wi-fi charger saves you from having to attach and disconnect cables repeatedly, the space over which vitality could be delivered this fashion is sort of brief. Certainly, it’s arduous to recharge or power a device when the air hole is only a few centimeters, a lot much less a couple of meters. Is there actually no sensible option to ship energy over better distances with out wires?
To some, the entire notion of wi-fi energy transmission evokes photos of Nikola Tesla with high-voltage coils spewing miniature bolts of lightning. This wouldn’t be such a foolish connection to make. Tesla had certainly pursued the thought of someway utilizing the bottom and ambiance as a conduit for long-distance energy transmission, a plan that went nowhere. However his dream of sending electrical energy over nice distances with out wires has endured.
To underscore how secure the system was, the host of the BBC science program “Bang Goes the Theory” caught his face absolutely into an influence beam.
Guglielmo Marconi, who was Tesla’s up to date, discovered easy methods to use “Hertzian waves,” or electromagnetic waves, as we name them at this time, to ship alerts over lengthy distances. And that advance introduced with it the potential of utilizing the identical sort of waves to hold vitality from one place to a different. That is, in any case, how all of the vitality saved in wooden, coal, oil, and pure fuel initially obtained right here: It was transmitted 150 million kilometers via house as electromagnetic waves—daylight—most of it thousands and thousands of years in the past.
Can the identical fundamental physics be harnessed to interchange wires at this time? My colleagues and I on the U.S.
Naval Research Laboratory, in Washington, D.C., suppose so, and listed below are among the the reason why.
There have been sporadic efforts over the previous century to make use of electromagnetic waves as a method of wi-fi energy transmission, however these makes an attempt produced blended outcomes. Maybe the golden yr for analysis on wi-fi energy transmission was 1975, when William Brown, who labored for
Raytheon, and Richard Dickinson of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (now retired) used microwaves to beam energy throughout a lab with better than 50 % end-to-end effectivity. In a separate demonstration, they have been capable of ship greater than 30 kilowatts over a distance of a couple of mile (1.6 kilometers).
These demonstrations have been half of a bigger NASA and
U.S. Department of Energy marketing campaign to discover the feasibility of solar-power satellites, which, it was proposed, would in the future harvest daylight in house and beam the vitality all the way down to Earth as microwaves. However as a result of this line of analysis was motivated largely by the vitality disaster of the 1970s, curiosity in solar-power satellites waned within the following many years, a minimum of in the USA.
Though researchers revisit the thought of solar-power satellites with some regularity, these performing precise demonstrations of energy beaming have struggled to surpass the high-water mark for effectivity, distance, and energy degree reached in 1975. However that scenario is beginning to change, thanks to varied current advances in transmission and reception applied sciences.
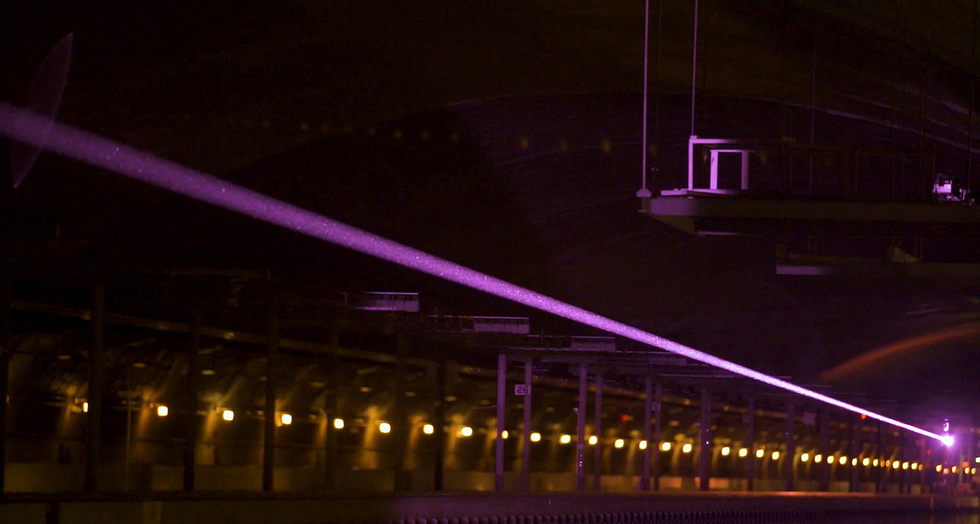

Throughout a 2019 demonstration on the Naval Floor Warfare Middle in Bethesda, Md., this laser beam safely conveyed 400 watts over a distance of 325 meters.U.S. Naval Analysis Laboratory
Most early efforts to beam energy have been confined to microwave frequencies, the identical a part of the electromagnetic spectrum that at this time teems with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and numerous different wi-fi alerts. That alternative was, partly, pushed by the straightforward incontrovertible fact that environment friendly microwave transmitting and receiving tools was available.
However there have been enhancements in effectivity and elevated availability of units that function at a lot increased frequencies. Due to limitations imposed by the ambiance on the efficient transmission of vitality inside sure sections of the electromagnetic spectrum, researchers have centered on microwave, millimeter-wave, and optical frequencies. Whereas microwave frequencies have a slight edge in terms of effectivity, they require bigger antennas. So, for a lot of purposes, millimeter-wave or optical hyperlinks work higher.
For programs that use microwaves and millimeter waves, the transmitters usually make use of solid-state digital amplifiers and phased-array, parabolic, or metamaterial antennas. The receiver for microwaves or millimeter waves makes use of an array of parts referred to as rectennas. This phrase, a portmanteau of
rectifier and antenna, displays how every factor converts the electromagnetic waves into direct-current electrical energy.
Any system designed for optical energy transmission would possible use a laser—one with a tightly confined beam, reminiscent of a fiber laser. The receivers for optical energy transmission are specialised photovoltaic cells designed to transform a single wavelength of sunshine into electrical energy with very excessive effectivity. Certainly, efficiencies can exceed 70 %, greater than double that of a typical photo voltaic cell.
On the U.S. Naval Analysis Laboratory, we have now spent the higher a part of the previous 15 years wanting into completely different choices for energy beaming and investigating potential purposes. These embrace extending the flight occasions and payload capacities of drones, powering satellites in orbit when they’re in darkness, powering rovers working in completely shadowed areas of the moon, sending vitality to Earth’s floor from house, and distributing vitality to troops on the battlefield.
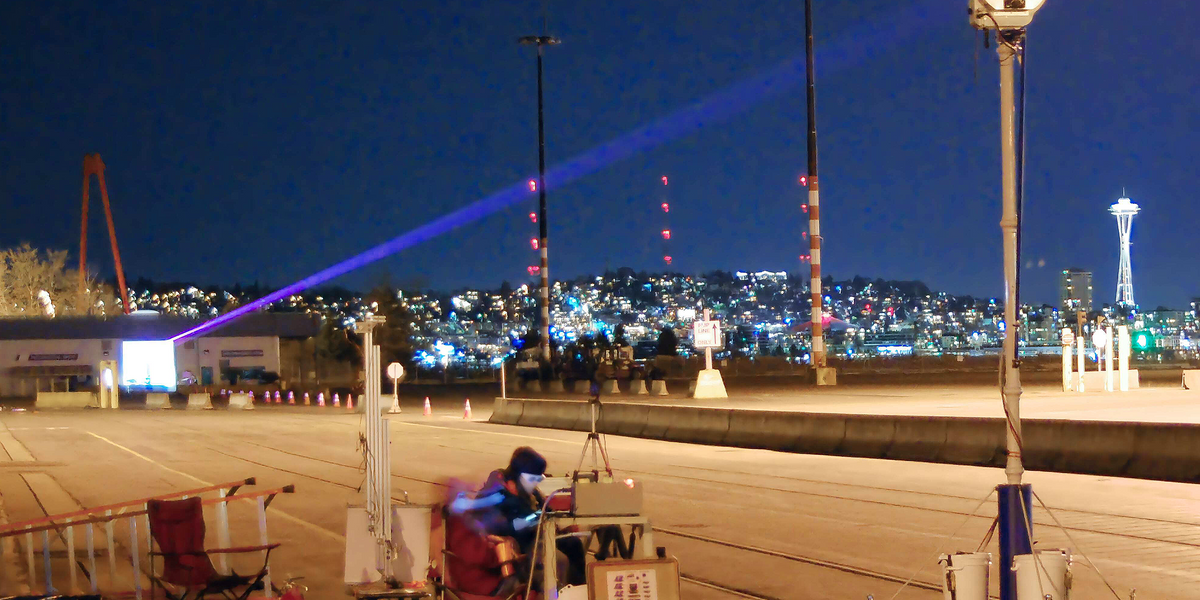
You would possibly suppose {that a} system for sending massive quantities of vitality via the air in a slim beam seems like a demise ray. This will get to the center of a vital consideration: energy density. Totally different energy densities are technically potential, starting from too low to be helpful to excessive sufficient to be harmful. However it’s additionally potential to discover a pleased medium between these two extremes. And there are additionally intelligent methods to allow beams with excessive energy densities for use safely. That’s precisely what a staff I used to be a part of did in 2019, and we’ve efficiently prolonged this work since then.
One in all our trade companions,
PowerLight Technologies, previously often known as LaserMotive, has been creating laser-based power-beaming programs for greater than a decade. Famend for profitable the NASA Power Beaming Challenge in 2009, this firm has not solely achieved success in powering robotic tether climbers, quadcopters, and fixed-wing drones, but it surely has additionally delved deeply into the challenges of safely beaming energy with lasers. That’s key, as a result of many analysis teams have demonstrated laser energy beaming over time—together with groups on the Naval Analysis Laboratory, Kindai University, the Beijing Institute of Technology, the University of Colorado Boulder, JAXA, Airbus, and others—however just a few have achieved it in a vogue that’s really secure beneath each believable circumstance.
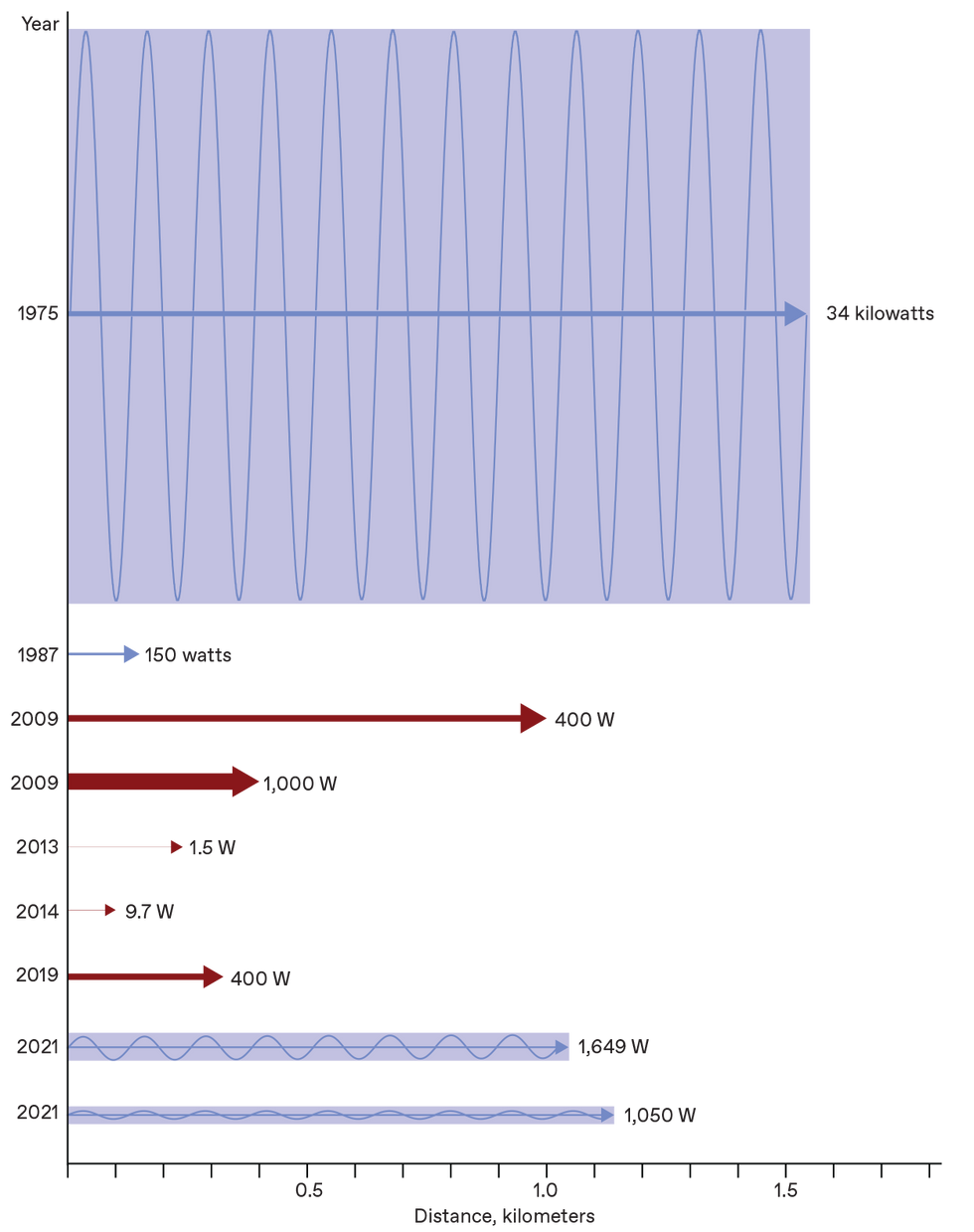
There have been many demonstrations of energy beaming over time, utilizing both microwaves [blue] or lasers [red], with the peak-power file having been set in 1975 [top]. In 2021, the creator and his colleagues took second and third place for the peak-power degree achieved in such experiments, having beamed greater than a kilowatt over distances that exceeded a kilometer, utilizing a lot smaller antennas.
David Schneider
Maybe essentially the most dramatic demonstration of secure laser energy beaming previous to our staff’s effort was by the corporate
Lighthouse Dev in 2012. To underscore how secure the system was, the host of the BBC science program “Bang Goes the Theory” caught his face absolutely into an influence beam despatched between buildings on the University of Maryland. This explicit demonstration took benefit of the truth that some infrared wavelengths are an order of magnitude safer on your eyes than different elements of the infrared spectrum.
That technique works for comparatively low-power programs. However as you push the extent increased, you quickly get to energy densities that elevate security considerations whatever the wavelength used. What then? Right here’s the place the system we’ve demonstrated units itself aside. Whereas sending greater than 400 watts over a distance that exceeded 300 meters, the beam was contained inside a digital enclosure, one that might sense an object impinging on it and set off the tools to chop energy to the principle beam earlier than any injury was performed. Different testing has proven how transmission distances can exceed a kilometer.
Cautious testing (for which no BBC science-program hosts have been used) verified to our satisfaction the performance of this function, which additionally handed muster with the Navy’s Laser Security Overview Board. In the course of the course of our demonstration, the system additional proved itself when, on a number of events, birds flew towards the beam, shutting it off—however solely momentarily. You see, the system displays the amount the beam occupies, together with its rapid environment, permitting the facility hyperlink to mechanically reestablish itself when the trail is as soon as once more clear. Consider it as a extra refined model of a garage-door security sensor, the place the interruption of a guard beam triggers the motor driving the door to close off.
The 400 watts we have been capable of transmit was, admittedly, not an enormous quantity, but it surely was ample to brew us some espresso.
For our demonstrations, observers in attendance have been capable of stroll round between the transmitter and receiver with no need to put on laser-safety eyewear or take some other precautions. That’s as a result of, along with designing the system in order that it may possibly shut itself down mechanically, we took care to contemplate the potential results of reflections from the receiver or the scattering of sunshine from particles suspended within the air alongside the trail of the beam.
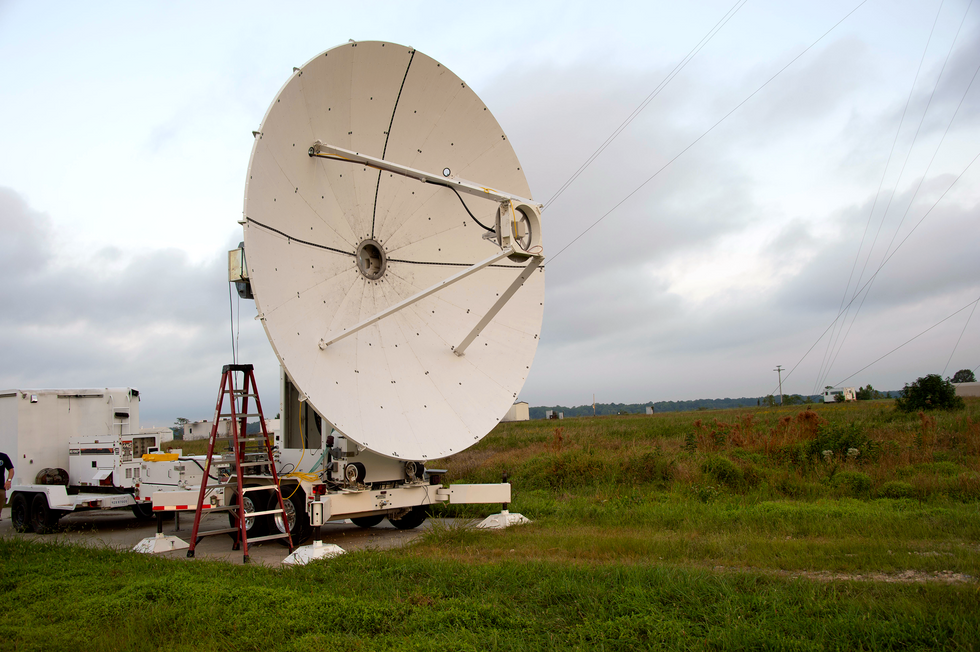
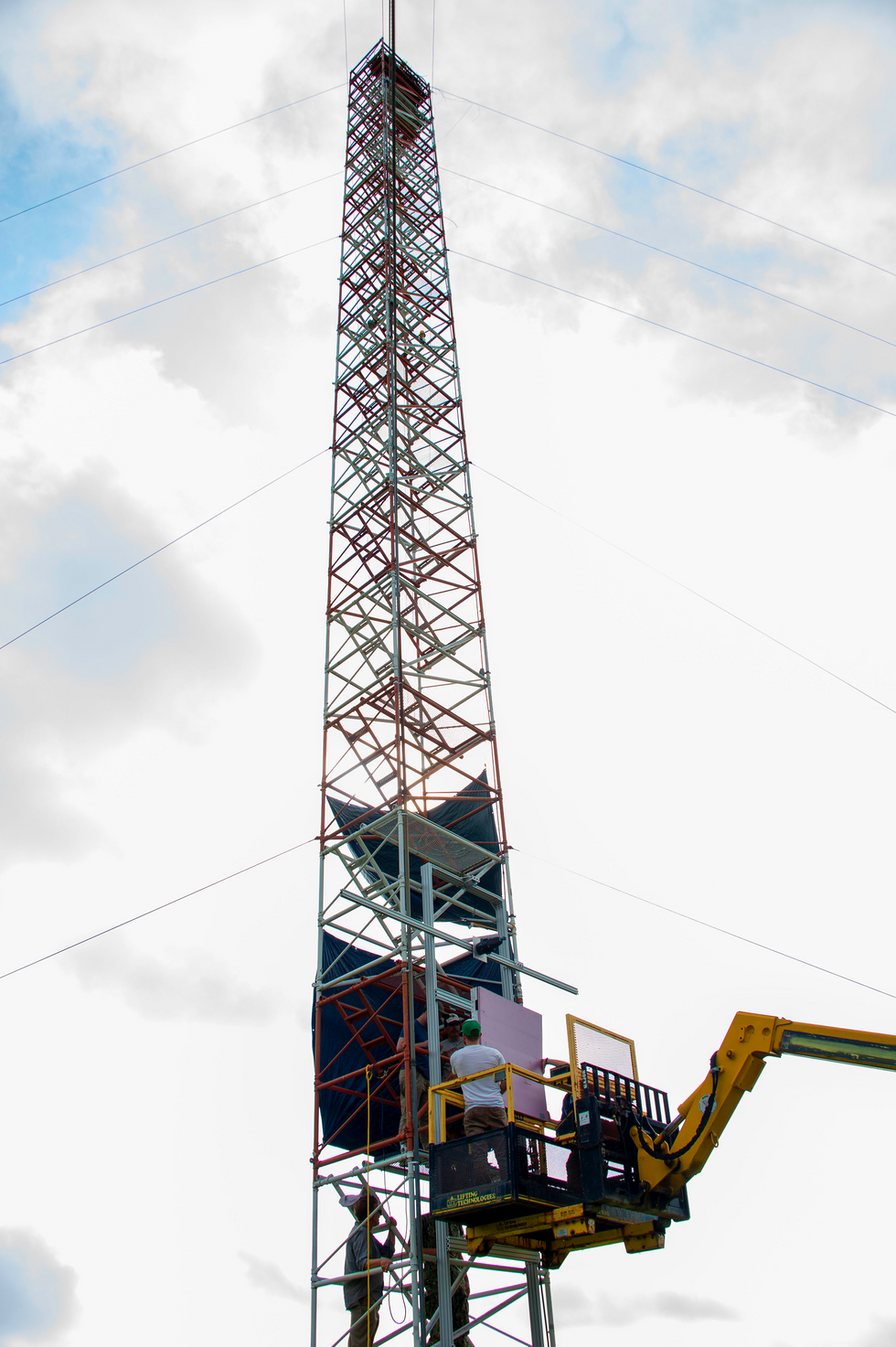

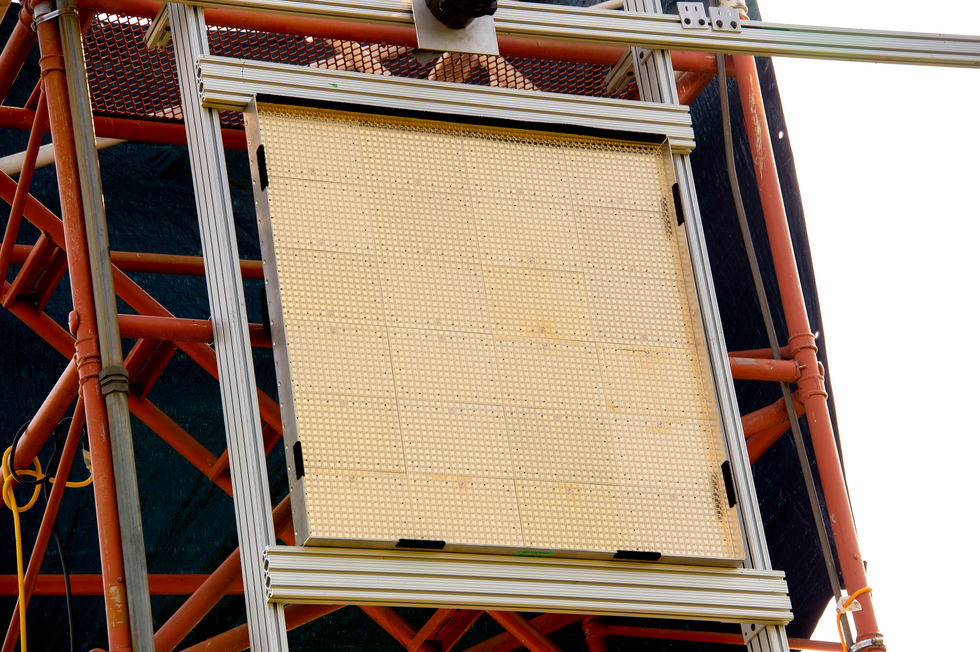

Final yr, the creator and his colleagues carried out an illustration on the U.S. Military’s Blossom Level take a look at facility south of Washington, D.C. They used 9.7-gigahertz microwaves to ship 1,649 watts (peak energy) from a transmitter outfitted with a 5.4-meter diameter parabolic dish [top] over a distance of 1,046 meters to a 2-by-2-meter “rectenna” [middle] mounted on a tower [bottom], which remodeled the beam into usable electrical energy.U.S. Naval Analysis Laboratory
The 400 watts we have been capable of transmit was, admittedly, not an enormous quantity, but it surely was ample to brew us some espresso, persevering with what’s change into de rigueur on this line of experimentation: making a sizzling beverage. (The Japanese researchers who began this custom in 2015 ready themselves some tea.)
Our subsequent aim is to use energy beaming, with absolutely built-in security measures, to cellular platforms. For that, we anticipate to extend the space coated and the quantity of energy delivered.
However we’re not alone: Different governments, established firms, and startups around the globe are working to develop their very own power-beaming programs. Japan has lengthy been a pacesetter in microwave and laser energy beaming, and China has closed the hole if not pulled forward, as has South Korea.
On the consumer-electronics degree, there are various gamers:
Powercast, Ossia, Energous, GuRu, and Wi-Charge amongst them. And the multinational know-how big Huawei expects energy beaming for smartphone charging inside “two or three [phone] generations.”
For industrial purposes, firms like
Reach Labs, TransferFi, MH GoPower, and MetaPower are making headway in using energy beaming to resolve the thorny downside of retaining batteries for robots and sensors, in warehouses and elsewhere, topped off and able to go. On the grid degree, Emrod and others are trying to scale energy beaming to new heights.
On the R&D entrance, our staff demonstrated throughout the previous yr secure microwave wi-fi energy transmission of
1.6 kilowatts over a distance of a kilometer. Firms like II-VI Aerospace & Defense, Peraton Labs, Lighthouse Dev, and others have additionally just lately made spectacular strides. At the moment, formidable startups like Solar Space Technologies, Solaren, Virtus Solis, and others working in stealth mode are working arduous to be the primary to realize sensible energy beaming from house to Earth.
As such firms set up confirmed monitor information for security and make compelling arguments for the utility of their programs, we’re prone to see entire new architectures emerge for sending energy from place to position. Think about drones that may fly for indefinite durations and electrical units that by no means should be plugged in—ever—and with the ability to present individuals wherever on this planet with vitality when hurricanes or different pure disasters ravage the native energy grid. Decreasing the necessity to transport gasoline, batteries, or different types of saved vitality can have far-reaching penalties. It’s not the one possibility when you possibly can’t string wires, however my colleagues and I anticipate, throughout the set of potential applied sciences for offering electrical energy to far-flung spots, that energy beaming will, fairly actually, shine.
This text seems within the June 2022 print difficulty as “Spooky Energy at a Distance.”
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net
Source link


